Infant skull fracture symptoms range from relatively insignificant to severely disabling. The symptoms include irritability, crying, lethargy, swelling or depression in the head, and seizures. Identifying the symptoms of a skull fracture in a baby is crucial for getting the child the prompt treatment and care they need.
What Is a Skull Fracture?
A skull fracture occurs when a physical force cracks a baby’s vulnerable skull during delivery. Babies’ soft, malleable skulls make it easier for them to pass through the birth canal. However, medical errors during delivery may predispose the baby to mild head injury.
Types of Skull of Fractures
The four main types of skull fractures include:
- Linear skull fractures: A linear skull fracture is a break in a cranial bone resembling a thin line without splintering, depression, or distortion of the bone.
- Depressed skull fractures: A depressed skull fracture is a break in a cranial bone with an evident depression of the bone skull.
- Diastatic skull fractures: Diastatic skull fractures occur when the cranial sutures are separated, most common from the lambdoid suture.
- Basilar skull fracture: A basilar skull fracture is a break of a bone in the base of the skull. Symptoms may include ear and eye bruises and hematoma(accumulation of blood) behind the eardrum. A cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak occurs in about 20% of cases and may result in fluid leaking from the nose or ear.
- Occipital skull fracture:An occipital fracture happens when the occipital bone near the base of the skull sustains abrupt, severe impact. The causes of skull fractures in the occipital region are Vehicle and bicycle accidents.
The occipital bone is a saucer-shaped bone at the base of the skull. A fracture of the occipital bone can be a potentially life-threatening injury.
They are often accompanied by further damage to the cervical spine and soft tissue structures, leading to severe complications or disability.
Causes of Skull Fractures in Infants
Medical malpractice during pregnancy frequently leads to pediatric skull fractures and future complications. Babies are particularly vulnerable because of the softness and malleability of their skull bones, which can result in severe brain injury. The presented symptoms vary from mild to severe. A pediatrician or traumatic brain injury specialist must identify the signs of skull fracture in babies and immediately commence treatment. The following are the causes of skull fracture in infants:
Fall
A shortfall usually causes a single, narrow, linear crack in the parietal bone in the back of the head. A young child can get a depressed skull fracture if they fall on an object or against a sharp edge from less than 5 feet away.
While most falls don’t cause any injuries, 31% of those that do result in an injury needs medical attention or activity restrictions for at least a day. The majority of these injuries are to the soft tissues, however between 10 and 15 percent of falls result in fractures, and 5 percent of falls end in more significant soft tissue injury or head trauma.
Medical error and malpractice
Infant skull fractures resulting from medical malpractice are due to forceps or vacuum extraction machine error. These tools help deliver babies efficiently when used correctly. A medical mistake can also occur in the absence of these delivery tools due to a healthcare provider’s negligence.
Accidents from sports and outdoor activities
Accidents from sports and other outdoor activities could cause a skull fracture in an infant.
Physical assault
Assault can sometimes lead to brain damage. Fights and arguments where someone gets punched in the head or hit with something.
Read on to learn more about infant skull fracture symptoms and how to treat them.
What Is a Traumatic Brain Injury?
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a form of acquired brain injury that occurs when a sudden accident causes damage to the brain. TBI can occur due to a violent direct blow to the brain or the brain hitting an object suddenly. This can cause severe damage to the brain tissues.
Can a Baby Recover From a Traumatic Brain Injury?
A child can recover from a traumatic brain injury with the right treatment plan. While children may sustain severe traumatic brain injuries, most children (up to 90%) that experience mild TBIs recover fast.
Is a Skull Facture Considered a Head Injury
Yes, Head Injury is damage to the head, skull, or brain. Head injuries can also be called brain injuries or traumatic brain injuries. A head injury can be as mild as a bruise, convulsion, or cuts around the head. Or it could be a concussion or traumatic brain injury. A head injury due to a skull fracture can lead to disabilities in children and deaths in severe cases.
Difference Between a Concussion and Contusion
Concussion
A concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury—or TBI—caused by a bump, blow, or jolt to the head or by a hit to the body that causes the head and brain to move rapidly back and forth.
Contusions
Contusions are one of the most common injuries occurring in active children. A contusion, or bruise, is caused by a direct blow to the body that can cause damage to the surface of the skin and deeper tissues, depending on the blow’s severity.
Symptoms of Infant Skull Fracture
Most mild fractures, fortunately, do not cause any long-term discomfort or pain. Fractures are sometimes missed because the initial symptoms are too subtle. Because skull fractures of infants are prevalent, their symptoms are very different depending on severity and type. Some common baby skull fracture symptoms include:
- Bleeding
- Brain damage
- Bruising
- Fatigue
- Syncope or loss of consciousness due to lack of blood flow to the brain
- Lump on the skull
- The distorted appearance of the skull
- Pallor
Newborns with more serious skull fractures may exhibit edema, a lump, or a depression on the head. Fluid or blood may ooze from the baby’s ears or nose, and there may be bruising around the baby’s eyes.
A more severe skull fracture may cause brain damage or a traumatic brain injury. The symptoms of a severe skull fracture include:
- Persistent pain in one’s head
- Continual nausea and vomiting
- An inability to focus or recall
- Disfluency in speech
- Struggle to Walk
- Isolated physical weakness in one arm, leg, or other parts of the body
- Bleeding from the nose or the ear
- Cuts and bruises near the eyes
- Bruising on the head, specifically in the aural canal
- Tinnitus: a sensation of fullness in the ears
- Poor vision and fainting
- Seizure
- Difficulty Waking Up
- Coma
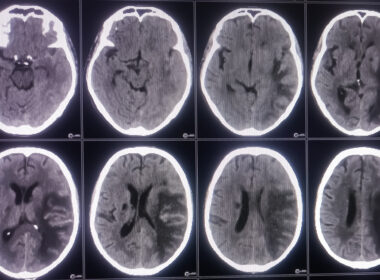
A CT scan or MRI may be performed to identify the location and extent of a skull fracture and to determine if it has caused a hematoma or bleeding on the brain if some of these symptoms are present.
Bleeding on the brain can put negative pressure on it and, depending on the severity, may or may not need to be drained surgically. This bleeding may cause lasting brain damage or even death in severe cases. Symptoms of a hematoma include anger, convulsions, and trouble sleeping or nursing.
How Can a Child’s Skull Fracture Be Diagnosed?
Babies who show signs of traumatic skull fractures must undergo a neurological examination. In a rare instance, a doctor ordered imaging tests to see a fractured artery.
Imaging procedures used for the diagnosis of infant skull fractures include:
- Blood tests and ultrasounds: Diagnostic tests that use invisible energy to produce images from the body through optical fibers.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): An MRI uses powerful radio waves and magnets to create a detailed view of the brain.
- Computerized tomography (CT) scan: This test is usually the first performed in an emergency room for a suspected traumatic brain injury for an in-depth evaluation of the infant skull.
Long Term Effects of Brain Damage in Infants
A skull fracture can lead to many long-term problems depending on how much brain tissue is damaged and how well it is treated. These chronic symptoms can manifest in a variety of ways, which include:
Cognitive impairment
Cognitive impairment is a term used to describe someone’s current condition. It manifests in various ways, including disorientation, dementia, low IQ, problems recognizing familiar faces or objects, and alterations in one’s emotional condition.
Delayed development
Delays in development that appear when an infant grows into a toddler may indicate brain injury. In addition, infants may experience symptoms such as lethargy, trouble sleeping, paralysis, or photosensitivity. Difficulties in receiving sensory information may also be indicative of brain injury.
Physical impairment
Physical signs of skull fracture that Infants exhibit include edema and a lump on the head. Bruising around the eyes is possible, as is discharge or blood from the baby’s ears or nose. When the skull is fractured more deeply, it might induce a traumatic brain injury or other forms of brain damage.
Altered behavior
One frequent assumption is that children with behavioral issues are more likely to have a traumatic brain injury.
In case of traumatic head injuries or whiplash (motor or vehicle accidents) in an infant, it causes damage to the internal organs, limbs, or blood. An injury on the brain directly under the point of impact is called a coup lesion.
Can Infants Skull Fractured Be Treated
The skull fractures of children can be treated depending on the injury’s severity. Surgery is performed in case of severe complications or edema. A mild skull fracture may be monitored and healed without additional treatment.
What Are Possible Complications of a Head Injury in a Child?
Children with severe brain injuries may have trouble hearing, feeling, or seeing depending on the severity and location of the brain damage. Sometimes, personality and behavioral changes are common complications.
Contact us at JustPoint to connect with one of our Birth Injury attorneys.
Add conclusion